Abstract: The effects of slice thickness, microwave power and loading on the microwave drying characteristics of bitter gourd were studied by single factor test. The microwave drying kinetics model of bitter gourd was established.
The results showed that the microwave power had the greatest influence on the drying of bitter gourd, followed by the loading, and finally the slice thickness. The microwave drying of bitter gourd accelerated the drying stage and slowed down the drying stage. The fitting of 7 commonly used thin layer drying dynamics mathematical models is obtained by comparing the correlation coefficient R2, the square of the residue and the RSS and the chi square χ2. The tian model is most suitable for describing the microwave thin layer drying process of bitter gourd slices. Above 0.99.
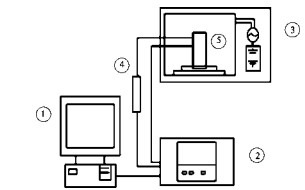
Key words: thin layer drying; microwave drying; drying characteristics; bitter gourd; kinetic model bitter gourd,
Cucurbitaceae Momordica, in addition to water, protein, fat, carbohydrates, crude fiber and various vitamins, bitter gourd also contains bitter gourd, protein-like active substances and a variety of amino acids and a variety of essential mineral elements, with heat Detoxification, nourishing blood and replenishing qi, replenishing the kidney and protecting the spleen, nourishing the liver and clearing the effect, is a therapeutic treatment for diseases such as fire, fever, dysentery and swollen sores in summer. Fresh bitter gourd has a water content of more than 90%, which is not easy to store at room temperature.