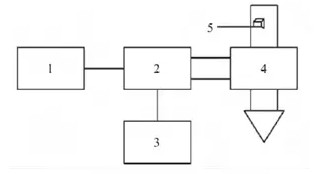
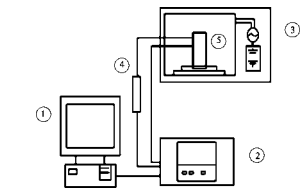
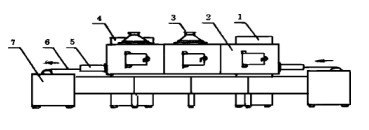
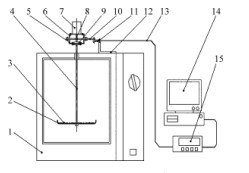
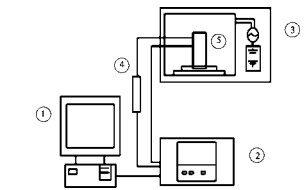
In this paper, the dielectric absorption power of wood microwave drying is derived from the RC model of wood microwave drying, and the drying mechanism is discussed from the perspective of spectroscopy, the temperature distribution is calculated, the existing problems in microwave drying are analyzed, and the solutions are put forward.
Keywords:
Keywords:
microwave dryer
Because the microwave energy penetrates into the wood interior, after the microwave energy is absorbed by the wood, the “heat accumulation” occurs in the wood interior, forming the so-called “positive heat source” of the wood interior temperature higher than the surface layer, which is different from the ordinary drying process. This is the biggest characteristic of microwave wood drying.
Because the microwave energy penetrates into the wood interior, after the microwave energy is absorbed by the wood, the “heat accumulation” occurs in the wood interior, forming the so-called “positive heat source” of the wood interior temperature higher than the surface layer, which is different from the ordinary drying process. This is the biggest characteristic of microwave wood drying.

So we can use microwave to dry special thick wood and special materials. However, microwave drying also has shortcomings. In order to ensure the quality of products, there are many technical problems to be further studied. The investment in drying equipment is too expensive, and the cost of electric energy consumption is too high. How to improve the economic efficiency needs further discussion.